The Advancement of Stainless Steel Cutting Technology in China
China has emerged as a global leader in stainless steel production and processing, particularly in the realm of stainless steel cutting technology. With decades of investment in research, advanced machinery, and skilled expertise, China's stainless steel cutting industry has gained a reputation for producing high-quality products for a wide range of applications. This article explores the growth, strengths, and applications of China’s stainless steel cutting technology and its increasing role in the global market.
A Rapidly Developing Industry
China’s stainless steel cutting industry has evolved rapidly over recent decades, driven by high domestic demand and global export opportunities. Leveraging cutting-edge technology, China has managed to excel in providing diverse solutions for both simple and complex stainless steel cutting requirements. These advancements are largely thanks to government support, collaborations with foreign technology providers, and a focus on modernizing equipment.
Key Cutting Technologies in China
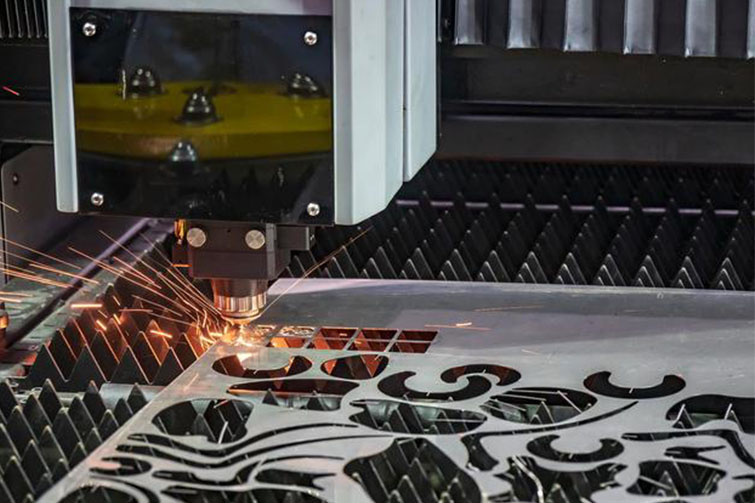
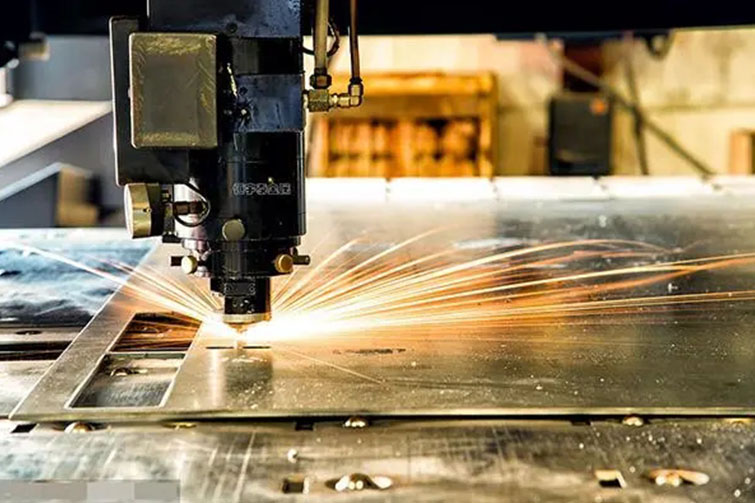
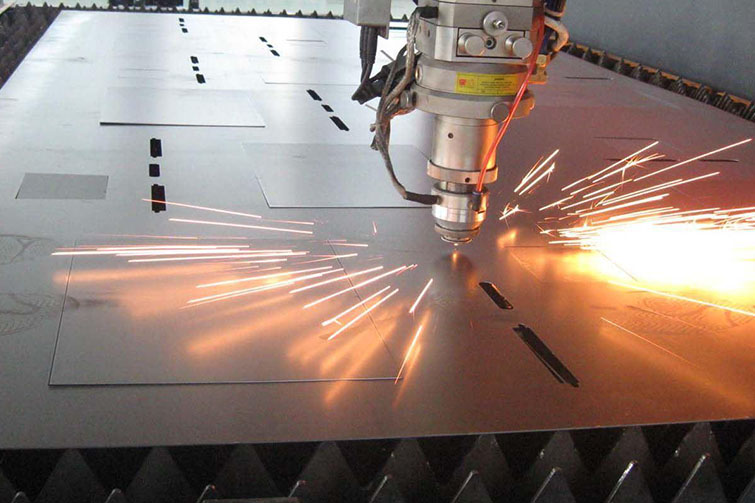
Laser Cutting Laser cutting is one of the most commonly used techniques in China’s stainless steel industry. Chinese manufacturers have mastered both fiber and CO2 laser cutting technologies, which provide precision and speed for various applications. Many factories use CNC (Computer Numerical Control) laser machines that allow for detailed, high-quality cuts, making them ideal for industries like automotive, electronics, and architecture.
Water Jet Cutting Chinese companies have also adopted water jet cutting for stainless steel applications, particularly for parts that require cold cutting to avoid heat distortion. This method is especially valuable for industries like aerospace and medical devices, where high-precision parts must retain their material properties without deformation.
Plasma Cutting Plasma cutting, known for its cost-effectiveness and speed, is widely used for stainless steel plates in China. Continuous improvements in plasma technology have made it possible to cut thicker and larger sections of stainless steel with high efficiency, making it a popular choice for construction and heavy machinery.
Mechanical Cutting and Sawing Traditional mechanical cutting methods such as band sawing, shearing, and punching remain prevalent for many industrial applications. These methods are ideal for high-volume production and cutting thicker steel sheets. Chinese manufacturers have invested in automating these processes, reducing labor costs while maintaining accuracy and consistency.
High Quality and Competitive Pricing
Chinese stainless steel cutting providers are known for their ability to offer competitive pricing without compromising quality. This is partly due to the scale of the industry and efficient supply chain management. Additionally, many manufacturers have obtained international certifications (such as ISO and CE), further ensuring the quality and compliance of their products.
Applications Across Diverse Industries
China's stainless steel cutting technology caters to a broad range of industries:
- Construction and Architecture: Precision-cut stainless steel components are used extensively in architectural structures and interior design.
- Automotive and Aerospace: The demand for high-precision parts has led to increased use of laser and water jet cutting technologies for vehicle and aircraft components.
- Medical Equipment: Stainless steel parts for medical devices require extreme precision, and Chinese manufacturers have developed cutting processes that meet strict international standards.
- Consumer Goods: Products like appliances, kitchenware, and even electronic casings benefit from China’s expertise in creating durable, finely crafted stainless steel components.
Future Trends and Innovations
The Chinese stainless steel industry is poised for further innovation. With the adoption of automation, AI-assisted cutting, and eco-friendly practices, Chinese manufacturers are optimizing their processes to reduce waste and improve efficiency. Smart manufacturing, which includes using AI for quality control and predictive maintenance, is also becoming a standard in the industry.
Moreover, as global demand for sustainable practices grows, many Chinese companies are shifting towards energy-efficient cutting technologies and recycling of waste materials. This commitment not only supports environmental goals but also strengthens China’s position as a preferred partner in global supply chains.
Conclusion
China’s stainless steel cutting technology has reached an impressive level of sophistication, providing competitive, high-quality solutions across various sectors. From advanced laser and water jet techniques to traditional mechanical methods, Chinese manufacturers offer a broad range of cutting options that meet international standards. As the industry continues to grow, fueled by innovation and a focus on sustainable practices, China’s stainless steel cutting sector will likely remain a strong contender in the global market for years to come.